Our Products
- Conveyor Accessories
- Conveying Equipment
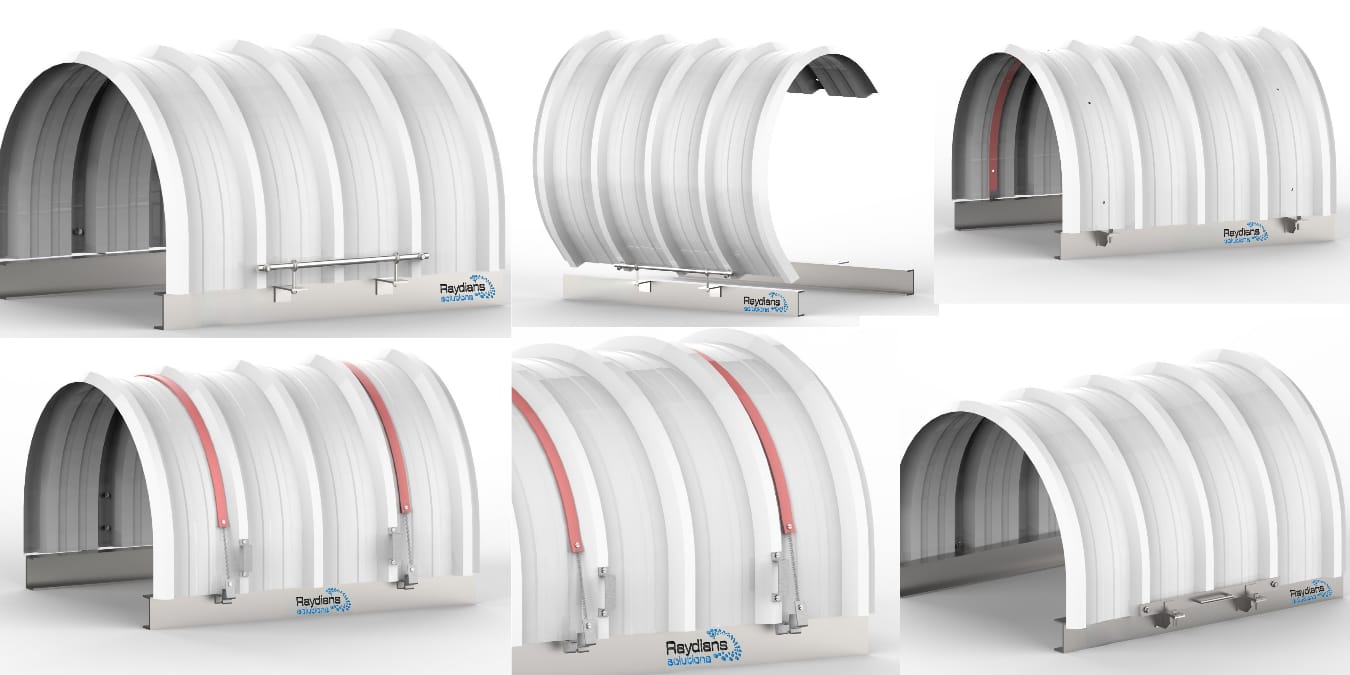
- Hood Cover
- Belt
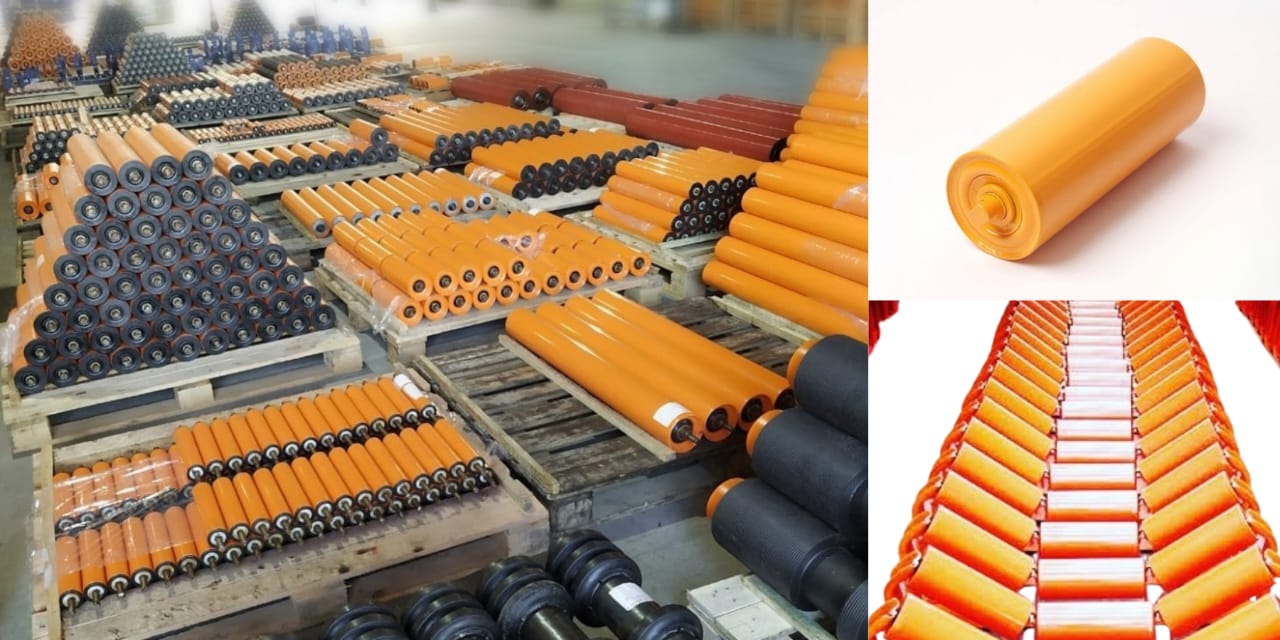
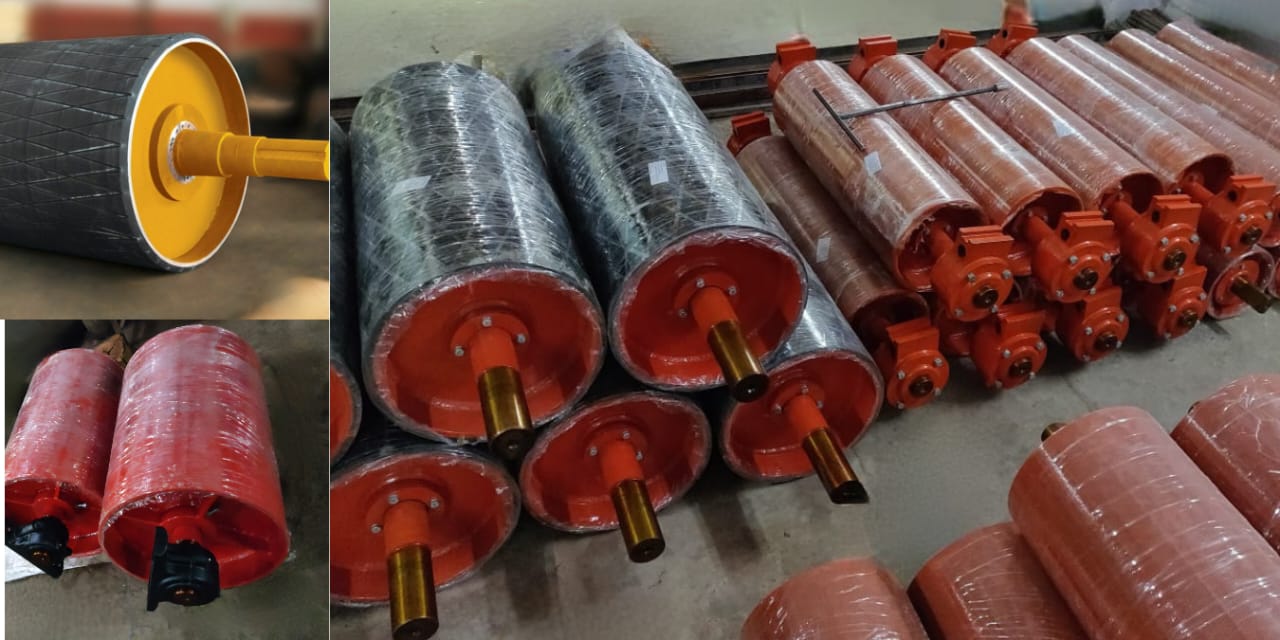
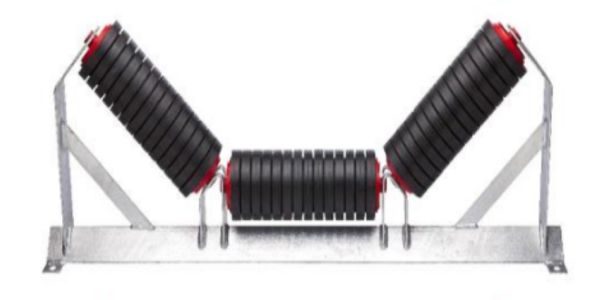
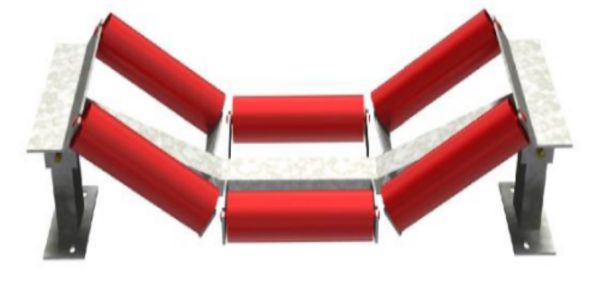
- Idlers Rollers
- Pulleys
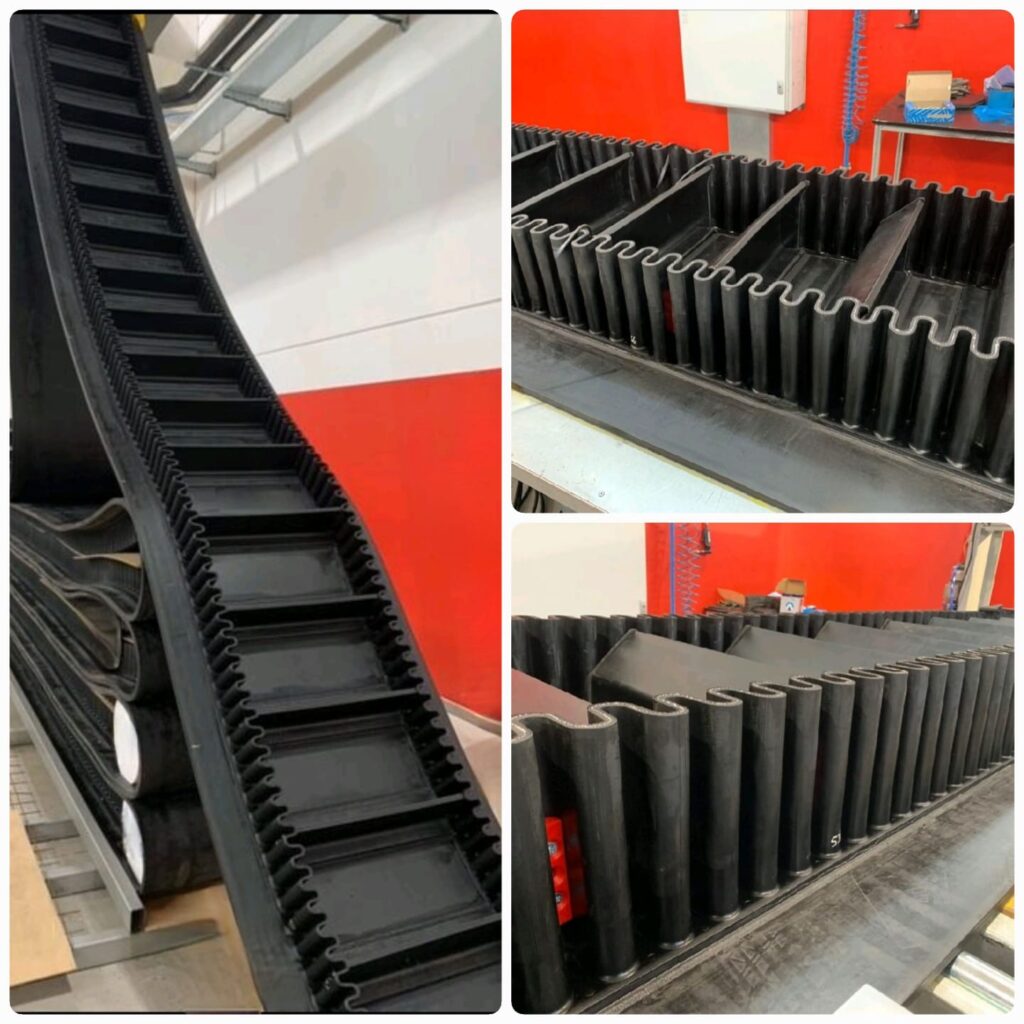



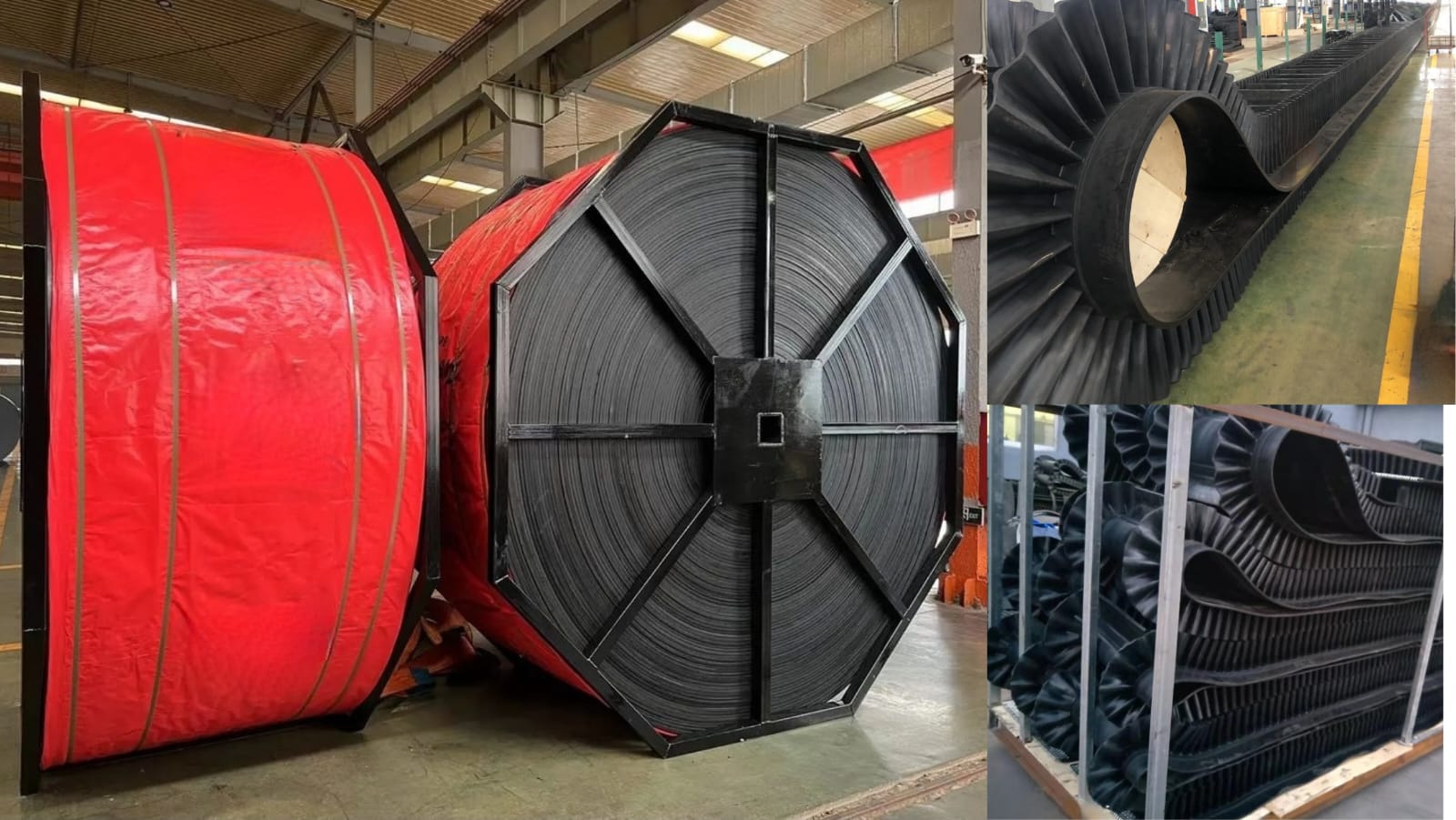
Side Walled Cleated Belts
These are special belts that are designed for Steep Angle conveyors also known as High Rise Belt conveyors. The belts are made from Steel Cord making it suitable for applications where space is a constraint. This also helps in reducing the overall conveying cost since the circuit lengths are significantly reduced.
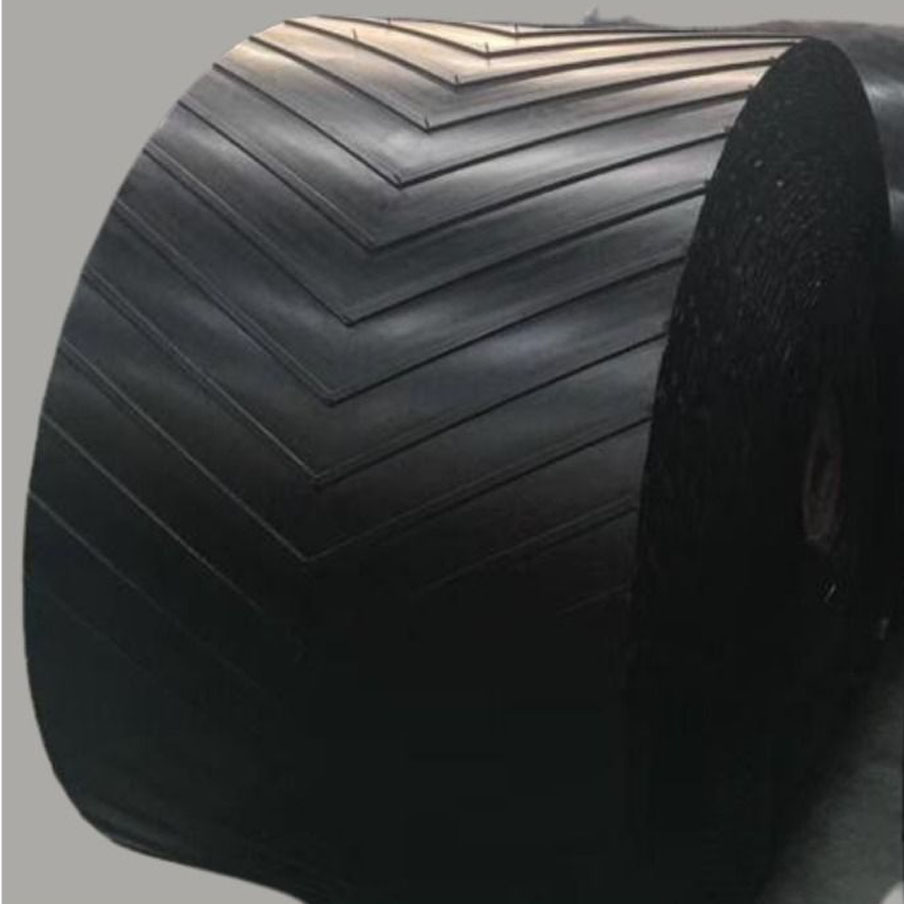



Chevron Cleated Belts
These belts are used in applications where the conveyors are designed at the maximum allowed inclination and sometimes even above the maximum allowed inclination angled to prevent the rollback of the material. These belts help to reduce the overall conveyor footprint and are available with flexible covers like Fire-resistant, heat resistant and Oil resistant.



Other Special Purpose Belts
Raydians range of Belts includes the following types: General Purpose Belts, Fire Resistant Belts, Oil Resistant Belts, Heat Resistant Belts (Up To 180 Deg. Celsius), Super Heat Resistant Belts (Upto 220 Deg. Celcius), Raydians Exclusive SHR (Upto 400 Deg. Celsius), Steel Cord Belts Impact Resistant Belts, Tear-resistant Belts
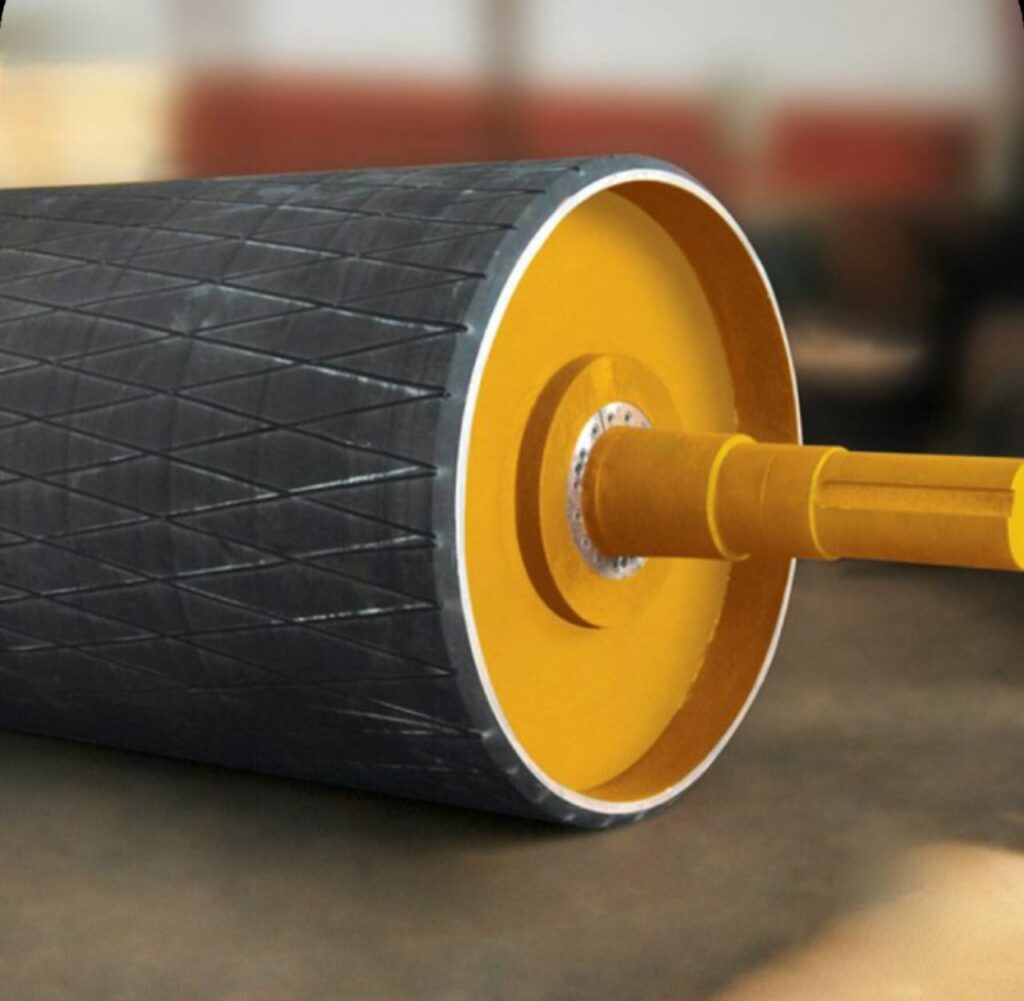




Pulleys
Raydians has the widest range of wear-resistant pulleys used to drive the conveyors. Head pulleys, Tail pulleys, Bend Pulleys, Snub and Take Up pulleys. Standard sizes and lagging types are shown below.





Pulleys
Raydians has the widest range of wear-resistant pulleys used to drive the conveyors. Head pulleys, Tail pulleys, Bend Pulleys, Snub and Take Up pulleys. Standard sizes and lagging types are shown below.
- Bucket Elevator
- Screw Conveyor
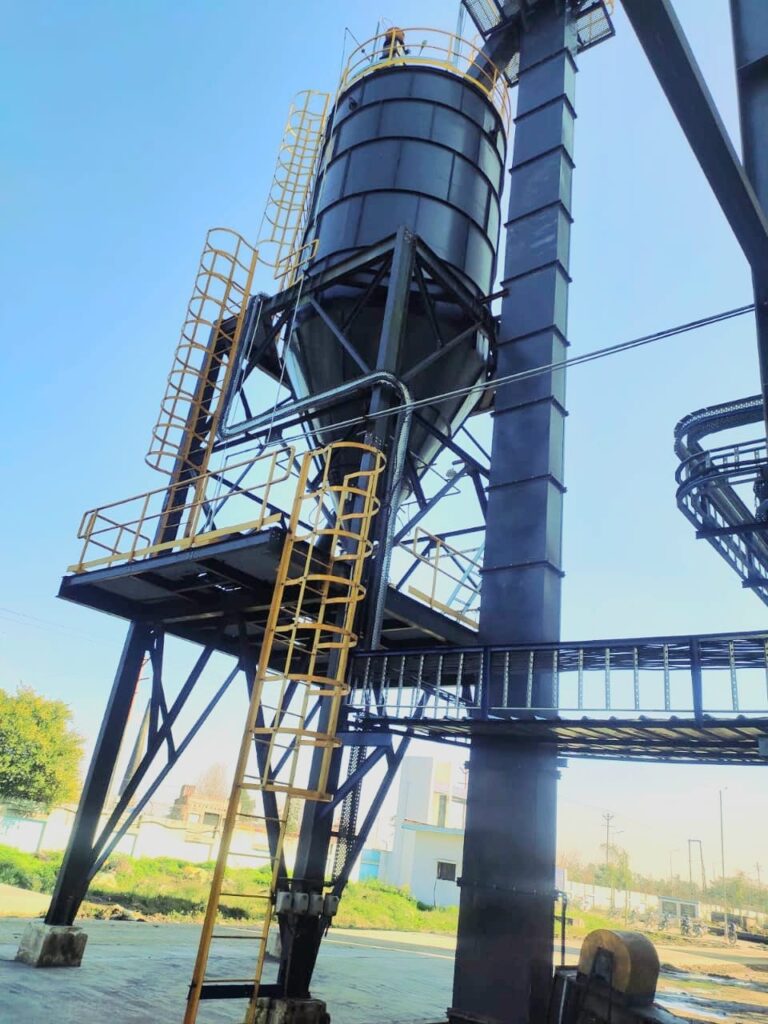





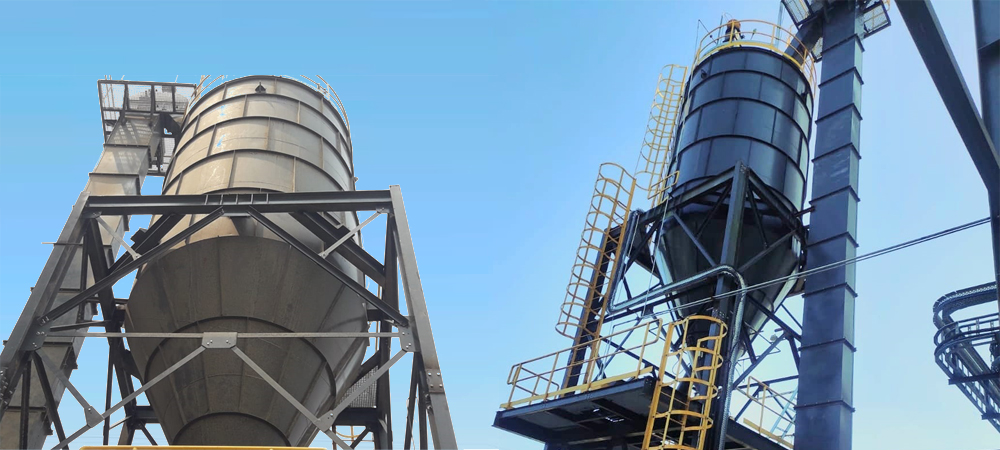
Bucket Elevator
Bucket Elevators are vertical conveying equipment used to convey materials upto 50mm size and capacities ranging from 500 kg per hour to 100 tonnes per hour for materials like lime powder, cement, coal, briquette, ash, rice husk, gypsum powder, talc, sawdust, woodchips, quartz powder, granite powder, sand, bitumin, cullet glass, pellets, soya husk, food grains, wheat, barley, maize, rice, corn, alumina, silica, phosphorus etc.





Bucket Elevator
Bucket Elevators are vertical conveying equipment used to convey materials upto 50mm size and capacities ranging from 500 kg per hour to 100 tonnes per hour for materials like lime powder, cement, coal, briquette, ash, rice husk, gypsum powder, talc, sawdust, woodchips, quartz powder, granite powder, sand, bitumin, cullet glass, pellets, soya husk, food grains, wheat, barley, maize, rice, corn, alumina, silica, phosphorus etc.
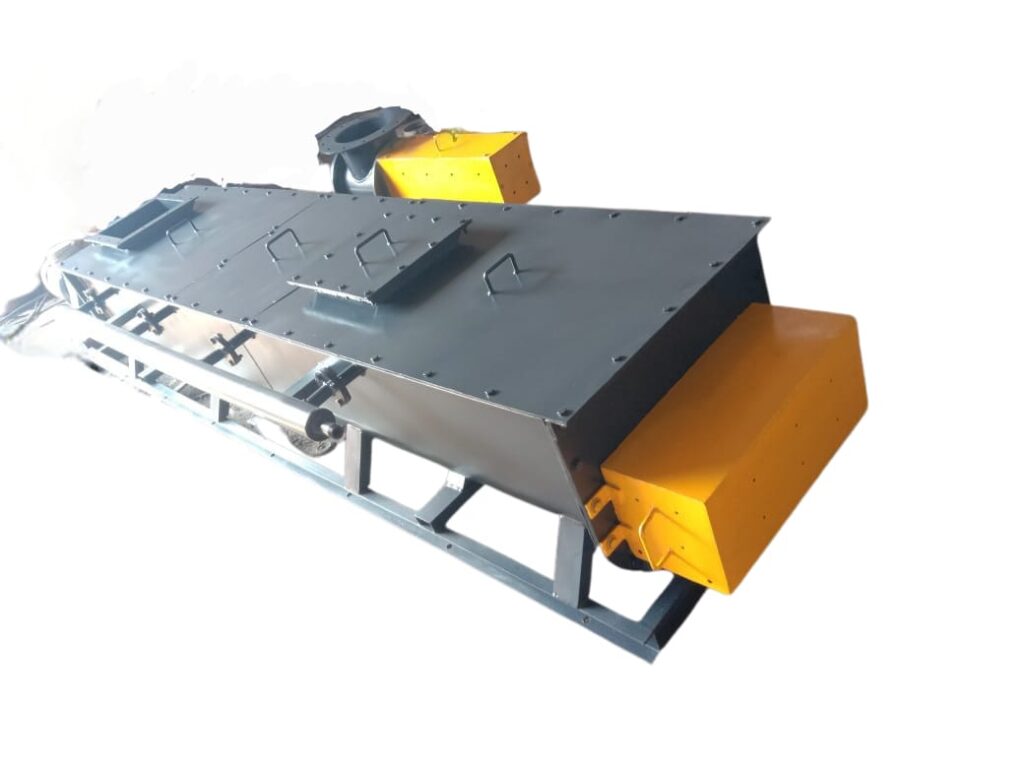





Screw Conveyor
A screw conveyor or auger conveyor is a mechanism that uses a rotating helical screw blade, called a “flighting”, usually within a tube, to move liquid or granular materials. They are used in many bulk handling industries. Screw conveyors in modern industry are often used horizontally or at a slight incline as an efficient way to move semi-solid materials, including food waste, wood chips, aggregates, cereal grains, animal feed, boiler ash, meat, and bone meal, municipal solid waste, and many others.
They usually consist of a trough or tube containing either a spiral blade coiled around a shaft, driven at one end and held at the other or a “shaftless spiral”, driven at one end and free at the other. The rate of volume transfer is proportional to the rotation rate of the shaft. In industrial control applications, the device is often used as a variable rate feeder by varying the rotation rate of the shaft to deliver a measured rate or quantity of material into a process.
Screw conveyors can be operated with the flow of material inclined upward. When space allows, this is a very economical method of elevating and conveying. As the angle of inclination increases, the capacity of a given unit rapidly decreases.





Screw Conveyor
A screw conveyor or auger conveyor is a mechanism that uses a rotating helical screw blade, called a “flighting”, usually within a tube, to move liquid or granular materials. They are used in many bulk handling industries. Screw conveyors in modern industry are often used horizontally or at a slight incline as an efficient way to move semi-solid materials, including food waste, wood chips, aggregates, cereal grains, animal feed, boiler ash, meat, and bone meal, municipal solid waste, and many others.
They usually consist of a trough or tube containing either a spiral blade coiled around a shaft, driven at one end and held at the other or a “shaftless spiral”, driven at one end and free at the other. The rate of volume transfer is proportional to the rotation rate of the shaft. In industrial control applications, the device is often used as a variable rate feeder by varying the rotation rate of the shaft to deliver a measured rate or quantity of material into a process.
Screw conveyors can be operated with the flow of material inclined upward. When space allows, this is a very economical method of elevating and conveying. As the angle of inclination increases, the capacity of a given unit rapidly decreases.
- Conveyor Accessories
- Hood Cover
- Belt
- Idlers Rollers
- Pulleys



Side Walled Cleated Belts
These are special belts that are designed for Steep Angle conveyors also known as High Rise Belt conveyors. The belts are made from Steel Cord making it suitable for applications where space is a constraint. This also helps in reducing the overall conveying cost since the circuit lengths are significantly reduced.



Chevron Cleated Belts
These belts are used in applications where the conveyors are designed at the maximum allowed inclination and sometimes even above the maximum allowed inclination angled to prevent the rollback of the material. These belts help to reduce the overall conveyor footprint and are available with flexible covers like Fire-resistant, heat resistant and Oil resistant.



Other Special Purpose Belts
Raydians range of Belts includes the following types: General Purpose Belts, Fire Resistant Belts, Oil Resistant Belts, Heat Resistant Belts (Up To 180 Deg. Celsius), Super Heat Resistant Belts (Upto 220 Deg. Celcius), Raydians Exclusive SHR (Upto 400 Deg. Celsius), Steel Cord Belts Impact Resistant Belts, Tear-resistant Belts





Pulleys
Raydians has the widest range of wear-resistant pulleys used to drive the conveyors. Head pulleys, Tail pulleys, Bend Pulleys, Snub and Take Up pulleys. Standard sizes and lagging types are shown below.





Pulleys
Raydians has the widest range of wear-resistant pulleys used to drive the conveyors. Head pulleys, Tail pulleys, Bend Pulleys, Snub and Take Up pulleys. Standard sizes and lagging types are shown below.
- Conveying Equipment
- Bucket Elevator
- Screw Conveyor





Bucket Elevator
Bucket Elevators are vertical conveying equipment used to convey materials upto 50mm size and capacities ranging from 500 kg per hour to 100 tonnes per hour for materials like lime powder, cement, coal, briquette, ash, rice husk, gypsum powder, talc, sawdust, woodchips, quartz powder, granite powder, sand, bitumin, cullet glass, pellets, soya husk, food grains, wheat, barley, maize, rice, corn, alumina, silica, phosphorus etc.





Bucket Elevator
Bucket Elevators are vertical conveying equipment used to convey materials upto 50mm size and capacities ranging from 500 kg per hour to 100 tonnes per hour for materials like lime powder, cement, coal, briquette, ash, rice husk, gypsum powder, talc, sawdust, woodchips, quartz powder, granite powder, sand, bitumin, cullet glass, pellets, soya husk, food grains, wheat, barley, maize, rice, corn, alumina, silica, phosphorus etc.





Screw Conveyor
A screw conveyor or auger conveyor is a mechanism that uses a rotating helical screw blade, called a “flighting”, usually within a tube, to move liquid or granular materials. They are used in many bulk handling industries. Screw conveyors in modern industry are often used horizontally or at a slight incline as an efficient way to move semi-solid materials, including food waste, wood chips, aggregates, cereal grains, animal feed, boiler ash, meat, and bone meal, municipal solid waste, and many others.
They usually consist of a trough or tube containing either a spiral blade coiled around a shaft, driven at one end and held at the other or a “shaftless spiral”, driven at one end and free at the other. The rate of volume transfer is proportional to the rotation rate of the shaft. In industrial control applications, the device is often used as a variable rate feeder by varying the rotation rate of the shaft to deliver a measured rate or quantity of material into a process.
Screw conveyors can be operated with the flow of material inclined upward. When space allows, this is a very economical method of elevating and conveying. As the angle of inclination increases, the capacity of a given unit rapidly decreases.





Screw Conveyor
A screw conveyor or auger conveyor is a mechanism that uses a rotating helical screw blade, called a “flighting”, usually within a tube, to move liquid or granular materials. They are used in many bulk handling industries. Screw conveyors in modern industry are often used horizontally or at a slight incline as an efficient way to move semi-solid materials, including food waste, wood chips, aggregates, cereal grains, animal feed, boiler ash, meat, and bone meal, municipal solid waste, and many others.
They usually consist of a trough or tube containing either a spiral blade coiled around a shaft, driven at one end and held at the other or a “shaftless spiral”, driven at one end and free at the other. The rate of volume transfer is proportional to the rotation rate of the shaft. In industrial control applications, the device is often used as a variable rate feeder by varying the rotation rate of the shaft to deliver a measured rate or quantity of material into a process.
Screw conveyors can be operated with the flow of material inclined upward. When space allows, this is a very economical method of elevating and conveying. As the angle of inclination increases, the capacity of a given unit rapidly decreases.